The Benefits and Risks of Ultra-Violet Radiation
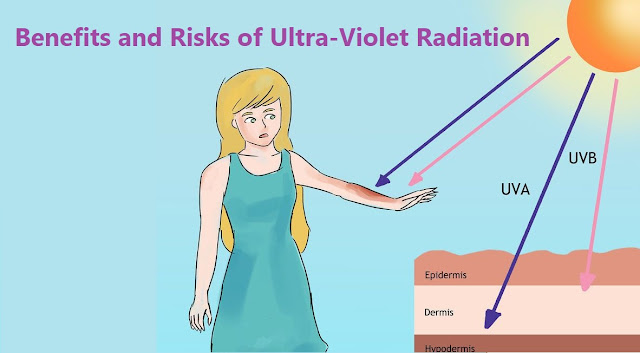
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a type of energy produced by the sun and some artificial sources, such as solariums. Ultra-violet (UV) lasers for Raman spectroscopy typically include laser wavelengths ranging from 244 nm through to 364 nm . UV radiation isn’t like the sun’s light or heat, which we can see and feel. Your senses cannot detect UV radiation, so you won’t notice the damage until it has been done. Theoretically UV Raman spectroscopy is no different from standard analysis using visible laser wavelengths. However, in practice there are a small amount that gets through has both positive and negative effects. Positive effects of UV Photolithography: UV is employed in fine resolution photolithography and hence is extensively used in the field of electronics. Vitamin D Production : UV from the Sun is needed by our bodies to produce vitamin D. Vitamin D helps strengthen bones, muscles and the body’...


