The Benefits and Risks of Ultra-Violet Radiation
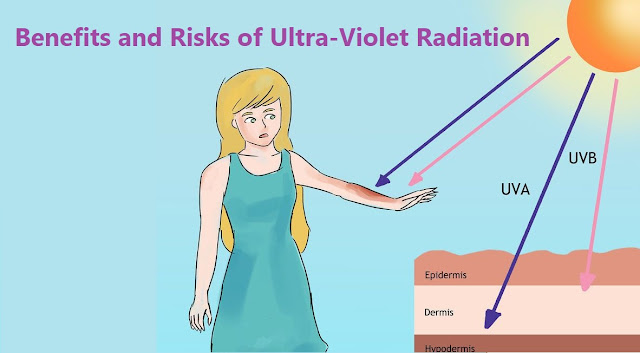
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a type of energy produced by the sun and some artificial sources, such as solariums. Ultra-violet (UV) lasers for Raman spectroscopy typically include laser wavelengths ranging from 244 nm through to 364 nm.
UV
radiation isn’t like the sun’s light or heat, which we can see
and feel. Your senses cannot detect UV radiation, so you won’t
notice the damage until it has been done.
Theoretically
UV Raman spectroscopy is no different from standard analysis using
visible laser wavelengths. However, in practice there are
a small amount that gets through has both positive and
negative effects.
Positive
effects of UV
- Photolithography: UV is employed in fine resolution photolithography and hence is extensively used in the field of electronics.
- Vitamin D Production : UV from the Sun is needed by our bodies to produce vitamin D. Vitamin D helps strengthen bones, muscles and the body’s immune system. It may also lower the risk of getting some kinds of cancers such as colon cancer.
- Fluorescent Lamps: When low-pressure mercury vapor is ionized, UV radiation is produced which is then absorbed by a phosphorescent coating in the inside of the lamp to convert to visible light. These lamps are used in the treatment of neonatal jaundice and psoriasis.
- In Genetics: The Green Fluorescent Protein is used as a marker in experiments in the field of genetics. Many substances, like protein are capable of absorbing UV and emit it at different wavelength and this property is employed in genetics, biochemistry and other related fields
- Sterilization: UV lamps have been employed to sterilize work spaces, laboratories, tools etc. UV radiation has been employed in drinking water treatment plants and waste water recycling projects as a viricide and a bactericide. It is also used in the food processing industry as a non-thermal tool for sterilizing food.
- It Helps some animals’ vision – Some animals (including birds, bees and reptiles) are able to see into the near UV light to locate many ripe fruits, flowers and seeds that stand out more strongly from the background. The fruits, flowers and seeds often appear quite different from how humans see them. For example, when seen in UV light, some flowers have different line markings, which may help direct bees and birds to the nectar.
- Checking Electrical Insulation and Fire Detection: Detecting pollution or degradation of insulation in an electrical device is carried out with the help of UV radiation. It is also employed in fire detectors.
Negative effects of UV
- Sunburn : Sunburn (or erythema) is redness of the skin, which is due to increased blood flow in the skin caused by dilatation of the superficial blood vessels in the dermis as a result of exposure to UV radiation. High UV doses may also results in edema, pain, blistering, and peeling of the skin a few days .
- Tanning :Tanning refers to delayed pigmentation of the skin, or melanin pigmentation. It usually becomes noticeable one to two days after exposure to the sun and gradually increases for several days persisting for weeks or months. Tanning results from an increase in the number of functions melanocytes (pigment cells) resulting in increased activity of the enzyme tyrosinase. This leads to the formation of new melanin and an increase in the number of melanin granules throughout the epidermis. Tanned skin need not only be considered a harmful effect as it does confer some protection for subsequent exposure to the sun, but the degree of protection is thought to be moderate and not sufficient as a sunscreen for Caucasian skin.
- Damages immune system – Over-exposure to UV radiation has a harmful suppressing effect on the immune system. Scientists believe that sunburn can change the distribution and function of disease-fighting white blood cells in humans for up to 24 hours after exposure to the sun. Repeated over-exposure to UV radiation can cause even more damage to the body's immune system. The immune system defends the body against bacteria, microbes, viruses, toxins and parasites(disease and infection). You can see how effective the immune system is by looking at how quickly something decays when it dies and the immune system stops working.
- Damages eyes – Prolonged exposure to UV or high intensities of UV (for example, in sunbeds) damages the tissues of eyes and can cause a ‘burning’ of the eye surface, called ‘snow blindness’ or photokeratitis. The effects usually disappear within a couple of days, but may lead to further complications later in life. In 1998, the Journal of the American Medical Association reported that even low amounts of sunlight can increase the risk of developing eye damage such as cataracts (which, left untreated, will cause blindness), pterygium and pinguecula. UV damage to the eyes is cumulative, so it is never too late to start protecting the eyes.


Comments
Post a Comment